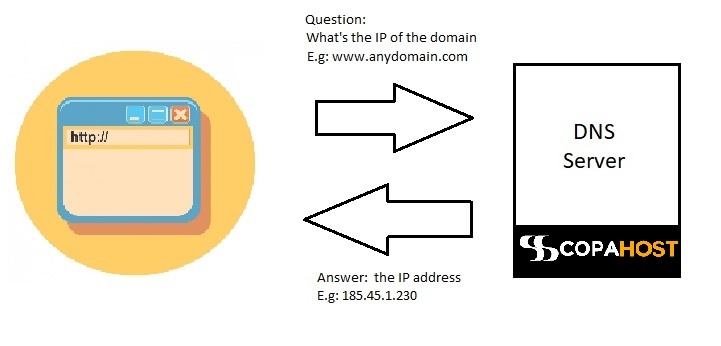
DNS stands for Domain Name System (RFC 2929). It is an internet service by which human-readable domain names (eg- www.abz.com ) are located and translated into machine-readable IP addresses (eg- 50.16.85.103). As an example, DNS may be considered as a phone directory. When we ask what does DNS stand for, we must keep in mind that it holds crucial information about the domain names. These domain names comprise of – email servers (MX records) and email validation protocols (DKIM, SPF, DMARC), TXT record verification, and SSH fingerprints. Thus, DNS works by keeping a record of every device that accesses the internet as per their IP addresses. For example, the basic DNS definition is a server that answers to your browser what is the IP address of a domain name.
How does DNS work?
The DNS protocol works just like querying a specific domain name for its IP address. This is called “DNS Lookup”. Whenever you try to open a URL in your web browser, it will query the DNS records for the IP address of the domain name (with a DNS Lookup). Then, the DNS server tells the IP address to your web browser. And finally, the browser establishes a connection with the webserver using this IP and asks for the specific content of the file and path of the requested URL.
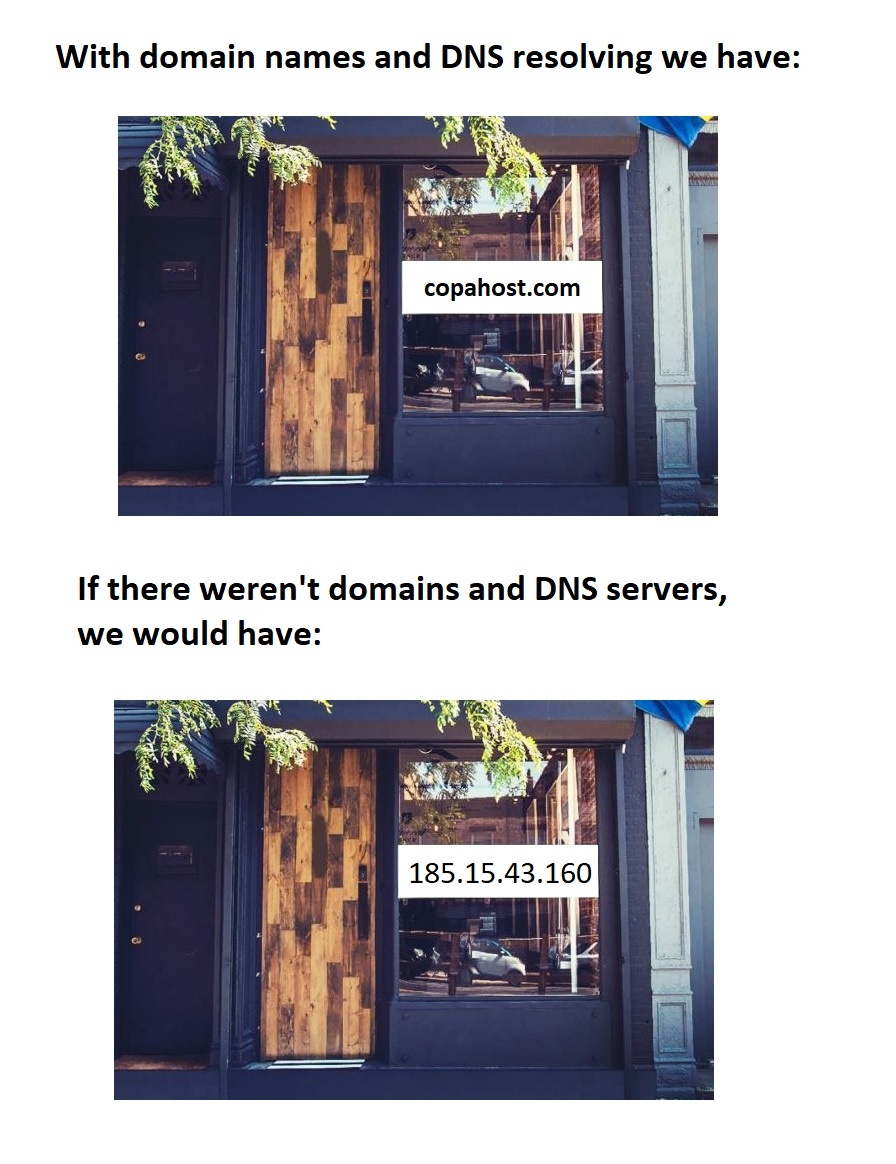
Above all, 99% of internet traffic is based on the TCP/IP protocol. This protocol only “talks” from IP to IP. A domain name (or a subdomain) is like a beautiful “front end” to make things easier for the customer.
For example, imagine if there weren’t DNS Servers in the world. Every store would give you a business card with their IP address just like: “185.15.43.160”.
Public DNS versus Private DNS servers
The DNS definition between public and private servers is very similar. The difference is only who can or can’t use them. Public DNS servers can resolve (answer) hosts for any connected customer. What does a private DNS stand for? A server only resolves hostnames of locally connected computers, servers or customers.
Public and Free DNS Servers examples
Some of the best public and free DNS servers include:
- Google (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4)
- Quad9 (9.9.9.9 and 149.112.112.112)
- OpenDNS (208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220)
Examples of domain name translating in a private DNS Server
Every time a user enters the domain name, DNS service translates it into the corresponding IP address. For a better understanding let’s explain.
For instance, a user enters the domain name “howstuffworks.com” in his/her browser. Soon after that, a request is made to the DNS server for resolving the domain name into an Internet Protocol (IP) address such as 70.42.251.42. This is how the process of DNS name resolution keeps on processing whenever it encounters a domain name.
What is a dynamic DNS server
Dynamic DNS (or DDNS) is a service that automatically updates your hostname with the current IP address of a server or a computer. This way, the dynamic DNS keeps on monitoring the IP addresses of your connection. Then, if the DDNS server detects any changes in your IP, then it automatically updates your DNS’s A (IPv4) or AAAA (IPv6) records.
This is useful for people who have an internet connection with a dynamic IP address (which changes every week, month or so..). By using a dynamic DNS server (or DDNS Server), you can have a permanent subdomain, always pointing to your current IP address. The dynamic DNS services stand for a system where the IP is often updated, where you use your subdomain whenever you need, and it will always point to your current IP… So, no matter if it changes!
There are some dynamic DNS services like No-ip.com and Dynu.com.
DNS definition: What does DNS stand for in networking
In terms of networking, DNS stands for Domain Name System (some may also call Domain Name Server). Both are correct DNS definitions. Whenever a user makes a visit to a website, the web browser “asks” the ISP what is the IP address of the domain name. A simple question? Yes, quite. The internet TCP/IP protocol works only by IP addresses. So, a domain name is just like a “front end” to an IP address of a server.
Certainly, the DNS system in networking is necessary to establish all the communications between servers.
What does DNS stand for in computing
In computing terms, DNS is an internet-based naming system used for converting the alphabetic names of web-based services into numerical forms, known as IP addresses. DNS naming system is used in networks operating on TCP/IP protocol. It identifies the computers and services through easy to use names.